Accounting is the most fundamental thing that is required to build any business and that’s why students need to master this. Keeping such importance in mind, professors keep giving assignments based on different accounting equations so that scholars become pro at solving it. To solve such questions, students need too much concentration and accuracy. And, that’s why they find it a daunting task and seek accounting assignment help. If you too are doubting your skills, then fortunately Global Assignment Help is here to provide you the best writing assistance for solving the accounting equations. But before that, you must know the basics of this subject. So, here it is.
What is Accounting?
Accounting is the process of recording the financial transactions of an organization. Along with recording, it also includes storing, sorting, summarizing, presenting, and retrieving of data. The result obtained after this step-by-step process is then presented in various reports and analyses.
The major purpose of accounting is to give a report over the financial information and know the performance, financial position, and cash flow of a business.
Key Elements of Accounting
To become master of accounting, you need to solve accounting equations. And to do this, you must know the key elements of accounting first. So, to measure the financial position of a company, there are three basic things to know. They are:
Assets
Assets includes what you or your organization owns. For example, cash, inventories, prepaid insurance, and investments.
Liabilities
It is something that the organization owes to someone other and have to pay in certain span of time. For example, loans, accounts or interest payable, and wages.
Capital
It is counted as the difference between assets and liabilities. So, the general equation derived after these three statements is,
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
Students also like to check: Understanding Cellular Respiration Equation
Steps to Solve Different Accounting Equations with Examples
There are mainly five types of accounting problems, they are:
- Accounting equation for a corporate.
- Accounting equation for a sole proprietorship.
- Calculating a missing amount within owner’s equity.
- Expanded accounting equation for a sole proprietorship.
- Expanded accounting Equation for a corporation.
Here, we have discussed each of them. Have a look.
1. Solving Equation for Corporate
The equation you need to follow for solving an accounting problem of corporation is:
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholder’s Equity
Example:
Let’s assume that several members of an organization invest a total of $20, 000 to start a company. In exchange, the corporation issues a total 2,000 shares of common stock. The effect on the corporation’s accounting is:
Asset ($20,000) = Liabilities (0) + Stockholder’s Equity ($20,000)
2. Accounting Equation for a Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the kind of business which is run by a single individual, and the equation need to solve the accounting problem on this is:
Assets = Liabilities (no effect ) + Stockholder’s Equity
Example:
Let’s assume, Mr. Bill is the sole proprietor of an organization. He invests funds of $20,000 to start a company. So, after this transaction, the accounting equation will be:
Assets ($20,000) = Liabilities (no effect) + Owner’s equity ($20,000)
3. Calculating a Missing Amount Within Owner’s Equity
Let’s assume that the net income of an organization for the year 2018 is unknown, but the amount of loans, initial and last balances are known. So, you can calculate the net income easily. Here we have provided an example to show it should be done.
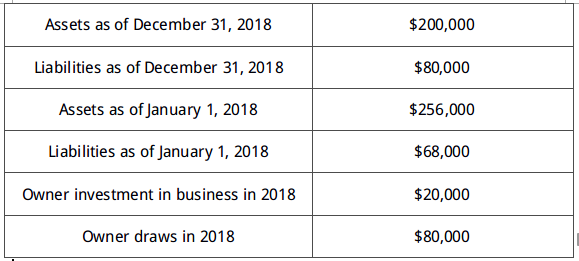
Step 1: Owner’s Equity on January 1, 2018 =$200,000 – $80,000 = $120,000
Step 2: Owner’s Equity on Dec, 31, 2018 = $256,000 – $68,000 = $192,000
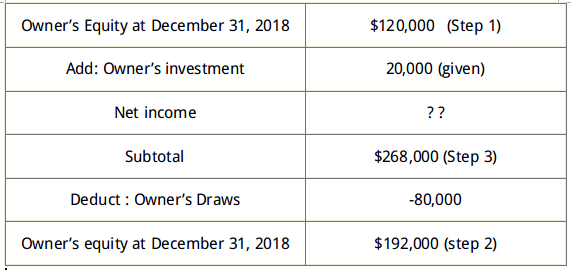
Adding Owner’s equity on Jan, 2018 and investments, ($120,000 + $20,000= $140,000),
Then subtracting the result ($140,000) from the subtotal, ($268,000 – $140,000 = $128,000).
So, the net income is $128,000.
4. Expanded Accounting Equation for a Sole Proprietorship
To solve the expanded accounting problem for sole proprietor, the equation that you should follow is,
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Capital + Revenues – Expenses – Owner’s Draws
Example
The expanded form of accounting problem for a sole proprietorship has been explained below.
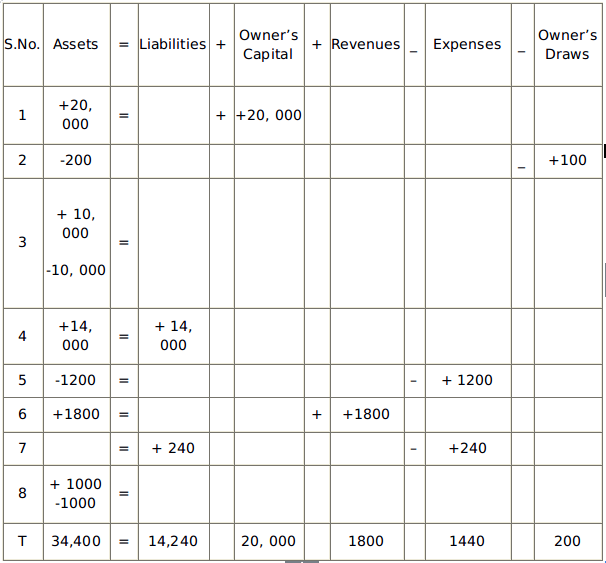
So, now you can calculate the net income.
Revenue - Expenses = Net Income
1800 - 1440 = 360
5. Expanded Accounting Equation For a Corporation
Here is the formula to solve the expanded accounting equation for a corporation.
Assets = Liabilities + Paid-in Capital + Revenues – Expenses – Dividends – treasury Stock
Example:
The same problem that we have solved in expanded accounting of sole proprietor, we will solve it here too as the expanded equation of a corporation. So, here it is.
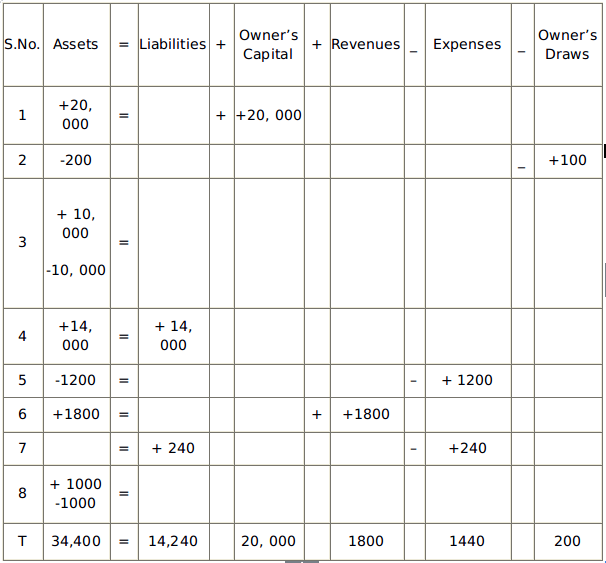
Here, you can also calculate the net income easily, just by subtracting the expenses from the revenue, i.e:
Revenue - Expenses = Net Income
1800 - 1440 = 360
So, these are five basic types of accounting equations. Hope you have found these solutions easy and accurate. You must have also understood what is accounting, its purpose, and key elements to do the calculations.
Check out these blog:
Free Tools
Easy to Use Paraphrasing Tool to Simplify Complex Academic Writing
Check Now
Get Structured Outline by Professionals for Your Dissertation
Check Now
Effortlessly manage citations and references with our smart referencing tool
Check NowPrice Calculator
- Plagiarism
- Pricing
- Order Now
- Call Back
- Live Chat

Limited Time Offer
Exclusive Library Membership + Free 300$ Wallet Balance

Get $300 Now
Update your Number























Thank you for submitting your comment on this blog. It is under approval. We will carefully review your submission and post it on the website.