Introduction
Finance is considering as one of the most crucial aspects for every business organization. The role of manager is to organize all sources of finance that essential of the performing all activity of the department (Bazley and et. al., 2013). Likewise, financial accounting is making an allowance for as appropriate field of accounting those are related with proper analysis and transaction pertaining to a business. This seems to be use for proper evaluation of various statements that are prepared by the department such as profit and loss statements, balance sheet and cash flow statement. These information is taken into consideration by different stakeholders that are linked with company to take valuable decision in regards to earn maximum profit in near future time.
This project is all about providing crucial information about concept of financial accounting as well as related regulation with them. Principles of accounting and regulations as well as concepts of material are discussed under this report in effective manner. Understanding of double entry bookkeeping, trail balance and accounting rules are used to record various transactions into the books of account. All the analysis is done through using proper information about various data that are used for reconciling control account as per the provided accounting data.
BUSINESS REPORT
Concept of financial accounting
In every business organization, it is necessary to make evaluation of various resources those are helpful for the company in proper planning for upcoming projects. In this manner, they can estimate total amount capital which will be going to incurred over them in more easy ways. Financial accounting is considering as one of the specialized branch of accounting that used to track company overall financial transaction those are done within an organization (Beatty and Liao, 2014). The main objective of accounting is to deliver certain information those are required for proper decision making in coming period of time. The role of manager is to prepare financial reports that are related with the firm's overall performance to outside stakeholders such as investors, creditors and other concern. Financial accounting process is done with the motive of using certain pre-determine rules and regulations that are issued through using standard norms like FASB, IASB and so on. The various companies used to select various accounting regulation that are framed by concern bodies such as US-GAAP, IFRS. These reports are made in order to keep every possible aspects as per the accounting standards. It is the primary duties of accountant to formulate financial statements with the use of ethical policies those are representing real picture of the company. There are various types of accounts those are formulate under the financial accounting in each year. Some of them are discussed underneath:
Incomes statement: As per these financial statements, company used to manage and operate their day to day transactions in effective manner. All the products those are related with the profit and loss statements are consists of earning, expenditure and profit they earn during an accounting period of time. It will assist organization in evaluating crucial aspects those are responsible for making profit and losses generated during the time (Bertoni and De Rosa, 2012).
Balance sheet: These statements used to provide crucial information about financial position of the department incurred during an accounting time. It is mostly prepared at the end of financial year. It consists of various head such as current assets, current liabilities and shareholder equity etc. This kind of statements used to provide specific information about financial health and future dependency of the company. On the basis of this statement, all the shareholders and top authorities would be liable to make their valuable decision in order to get better outcomes in near future time. All organization and various investors need to correct these financial statements for getting loans and investing in other companies. We also provide assignment writing services to UK students
Cash flow statements: According to this particular statements, it has been seen that proper evaluation of total cash inflows and outflows generated during the time within an organization is determine in effective manner. Only cash related information or transaction those are collected from various activities such as operating, investing and financing are taken into account. This statements used to assist in managing various cash in the company those are gather from various sources (Bhattacharyya, 2012).
Rules and regulation associated with financial accounting
There are various norms and policies those are related with the accounting rules that are helpful for the controlling of various financial outcomes. Accounting is considering as one of the systematic process of an organization that is having essential aspects associated with the financial tools and transaction that are generated by company in their regular course of operations. The IASB provide valuable explanation of conceptual framework for financial reporting is that, the main motive of financial reports of an organization is to delivery specific information about the financial position and cash availability of the company. These detail data would be reliable for various stakeholders and other potential investors to make future investment decision in effective manner (Biondi and Zambon, 2013). All the financial users are needed to have diversified group of accounting that deals in better profitability in coming period of time. To maintain or use regulations as per the mentioned bodies FASB, IASB are taken into consideration. These bodies are associated with certain standards for formulation of statements through using accounting standard like as various accounting norms like IFRS and GAAP standards are needed to be taken into consideration. The Accounting board need to deliver effective rules and regulation for the formulation of financial statements. These kind of standard used to guide essential aspects that assist managers and accountant in development of appropriate accounting report to the company.
Principles and regulations of accounting
Accounting principles are said to be effective rule as well as guidelines that every company need to implement during reporting of financial data. There are various number of basic accounting standards that develop through common usage (Carmichael and Graham, 2012). The application of principles through accountant must make sure that every financial record is having both informative and reliable. All the data those are gathered from various sources of the department are taken into use in effective manner for the preparation of financial statements. Few common accounting aspects which will be taken into account because it, consists of various aspects such as revenues, expenses, assets and other profit and loss statements. There are large number of conceptual aspects those are required to be estimate in order to make firms more beneficial for future time frame. The main aim of accounting is to deliver reliable accounting, reporting and analyzing financial data in effective manner. Certain types of accounting norms that are used for the purpose of analyzing business transactions those are done during the period of time. Some crucial accounting rules are mentioned underneath:
- Personal account: This has been used to determine accounting transaction which will be related to an individual or organization at the same point of time. In this the rules says that, debits all the receivers and credit amount to giver. Few common examples are capital and drawings.
- Real account: As per this accounting rules which is related with tangible and intangible assets of goods. In this rule, debit what comes inside the business and credit what goes out from the business. Examples, plants and machinery.
- Nominal account: According to this financial transaction that are done during each accounting period till accomplishment of time frame. In this debit all the income and loss and credit all expenses. Examples, salary and dividend (Edwards, 2013).
Principles of accounting: There are different types of principles that used to develop by using common usage. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Full disclosure: It is needed for the company to provide vital data requirements that every customer must accustomed to learn financial aspects those are consider for effective decision making. The role of managers is to make sure that every detail information about all transaction that are recorded into the statements must be showing clear image of the company.
- Going concern principles: It has been found that business must be operating for longer period of time. This means that every transaction that are related with the company must be utilize proper resources and entries into right manner. The all financial transaction is needed to keep into their respective account of the company (Fülbier and Weller, 2011).
- Cost principles: This happens to be one of the effective rules of accounting, it means that all the transactions which are done by the company must be related to cash only. The recording need to be done on the basis of historical and cost principles basis. The cost principle required that all assets must be recorded as per their time and cost.
There are diverse kinds of accounting conventions that are accountable for enhancing an entire growth and profitable for the firm. Here are some of them are:
Consistency: Organization would require to adopt efficient accounting tools which ultimately adjust on the regular basis. Modifications are accessible only in those kinds of situations under which advanced methods is emerged into the consideration in highly effective manner. This will demonstrate on the genuine and reliable components of financial position of the organization. Few of the examples of implementing this is to identify that if the cited organization would implement straight line methods and will not changes at reducing balance method in other period of time (Gassen, 2014).
Materiality: This is reliable on immaterial costs which could be aggregated along with an amount of common nature or operations of the cited firm. This is relied upon the total size and nature of their products that occurred during the time. Target might be adequately in an effective manner which could causes agents to apprehend opinion of convening business in highly reliable way to enhance an entire growth for the profitability for the company. Importance of the occasion is to be demonstrated efficiently into their respective manner (Horngren and et. al., 2012).
Concept:
- Money measurement: Under this concept, whole of the transactions in the businesses are recorded in relation to the money implemented in a company. This is implemented in order to render an effective aspect of knowing performance of the organization. Skillfulness of administration which will not be disclosed in the account (May, 2013).
- Prudence/ Conservatism: Total earnings and revenues are not awaited. This does not have basic concept of addressing expenses and debt in case there is uncertainty which are associated with justifiable outcomes, but to enhance which are confident of being trained (Phillips and et. al., 2011.).
CLIENT 1
P1 Double entry and book keeping system debit and credit records of sales and purchase
Double entry system
It is the method that renders structure and medium of recording transactions and incidents in a particular manner. Here are specific kinds of information that are implemented for running of operations and management. Book keeping systems ascertain to identify the effect of transactions. According to book keeping system, each of the business transaction has an adverse impact two side of accounts. There is a description.
Ledger posting:
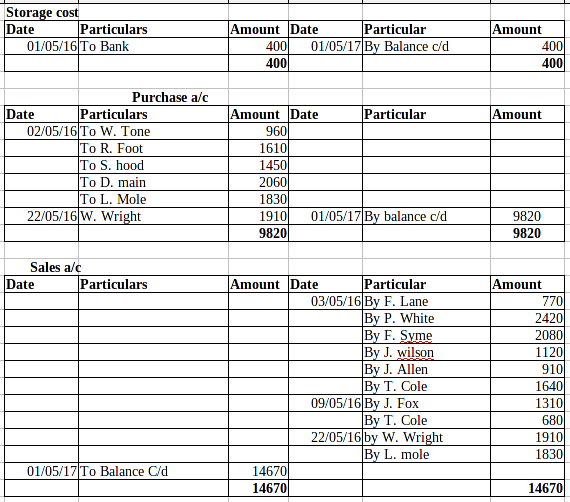
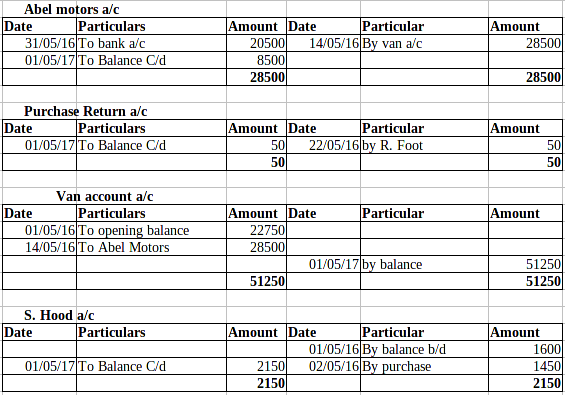
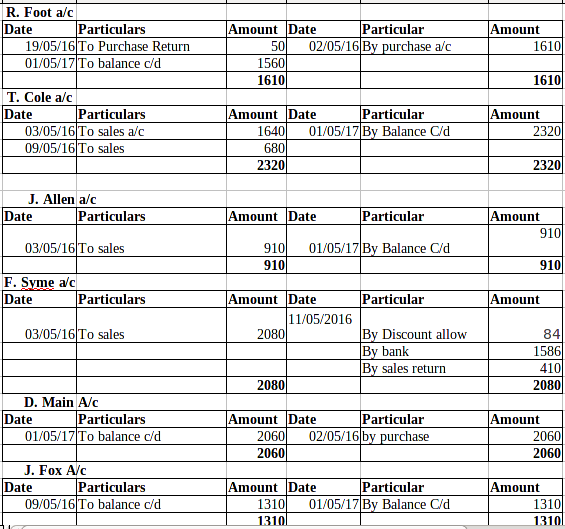
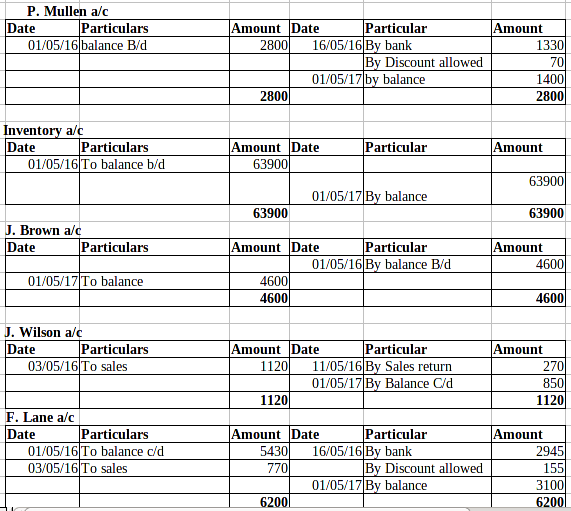
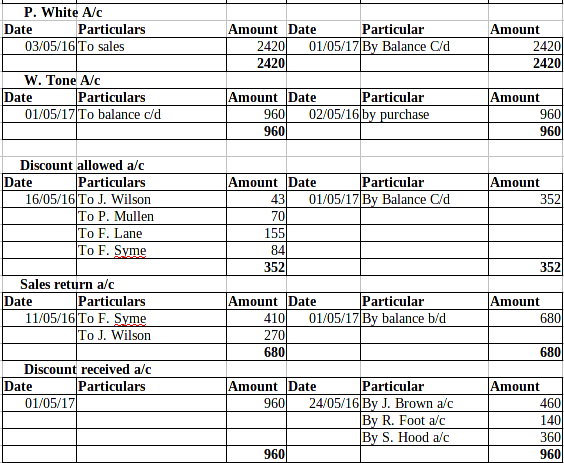
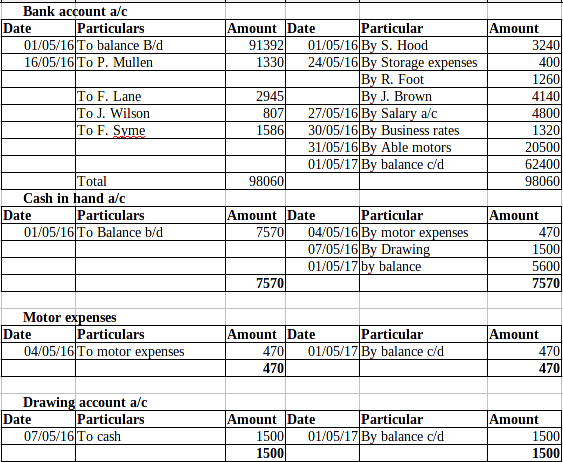
P2 Trial balance implementing the use of balance rule to done the ledger:
Trial Balance: This is the method under which all the transactions which are being recorded in the journal and ledgers have been posted in the trail balance in order to check adequacy of the debit and credit balance. Now, this can be rightly said that the management must use this technique in order to know about the availability of the balance in an effective manner. The balance of the debit and debit side must be equal (Ryder and ElaineRyder, 2012).
CLIENT 2
a). Profit and loss statement for the Peter piper
Profit and loss statement of Peter Piper for the year ended 31st December 2017
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
| To Opening stock | 82200 | By sales a/c | 1215000 |
| To wages and salaries (177500+1220) | 178720 | ||
| To Purchase a/c | 778800 | ||
| To Gross Profit | 276920 | By closing Stock | 101640 |
| 1316640 | 1316640 | ||
| To motor expenses | 87400 | By Net Profit | 276920 |
| To Heating and lighting | 4950 | ||
| To Depreciation | |||
| on freehold primes 4650 | |||
| on equipments 7500 | |||
| on Vehicle 2800 | 14950 | ||
| To Advertisement expenses | 4810 | ||
| To administration expenses | 17650 | ||
| To net profit | 147160 | ||
| 276920 | 276920 |
(b) Financial Position Statements
| Particulars | Amount (figures in £) |
| Current assets | |
| Inventory | 101640 |
| Prepaid advertisement expense | 8470 |
| Trade receivables | 106960 |
| Cash in hand | 2440 |
| Total current assets | 219510 |
| Free Hold Premises | 270000 |
| Equipments | 172500 |
| Vehicle | 28000 |
| Total non current assets | 470500 |
| Total assets | 690010 |
| Liabilities and equities: | |
| Current liabilities | |
| Trade payable | 76910 |
| Bank overdraft | 11290 |
| Out standing salary | 1220 |
| Accumulated depreciation(42150+105000+16800) | 163950 |
| Total current liabilities | 253370 |
| Capital 332120 | |
| Add: profit 147160 | |
| Less :- drawings (42640) | 436640 |
| Total equities and liabilities | 690010 |
CLIENT 3
P4 Prepare final accounts for a range of examples contains sole traders, partnerships or limited
a) Profit and loss statement of Raintree Ltd. For the year ended 30th September 2017
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount (Figures in £) |
| To Opening stock | 17000 | By sales a/c | 105000 |
| To Purchase a/c | 32000 | ||
| To Gross Profit | 74000 | By closing Stock | 18000 |
| 123000 | 123000 | ||
| To Distribution cost | 19000 | By Net Profit | 74000 |
| To Depreciation | 15000 | ||
| To Corporate Charges | 4000 | ||
| To administration expenses | 30000 | ||
| To net profit | 6000 | ||
| 74000 | 74000 |
(b) Statement of financial statement of Braintree Ltd.
| Particulars | Amount (Figures in £) |
| Current Assets | |
| Inventory | 18000 |
| Trade receivables | 24000 |
| Prepaid warehouse rent | 3000 |
| Bank | -15000 |
| Total current assets | 30000 |
| Non Current Assets | |
| Land and building | 60000 |
| Plant and equipment | 65000 |
| Total non current assets | 125000 |
| Total assets | 155000 |
| Liabilities and equities: | |
| Current liabilities | |
| Trade payables | 14000 |
| Outstanding administration cost | 2000 |
| Provision for tax | 37000 |
| Corporate Tax | 4000 |
| Total liabilities | 57000 |
| Equity | |
| Share capital @ £1 each | 50000 |
| Share premium | 20000 |
| Retained earnings | 22000 |
| Profit | 6000 |
| Total equity | 98000 |
| Total equities and liabilities | 155000 |
C). Accounting concepts
Consistency: This idea characterizes property of book-keeping approaches and calculating in long term view. As directed by this idea book-keeping adjustments and strategies ought to be stay consistent for the forthcoming years and length and ought not to very in here and now term. In the above mentioned situation, this is rightly said that link use reducing strategy for devaluation on the hardware and Raintree Ltd ought to take after this tool for demonstrating further.
Prudence: - This is ideas which talk about materiality and significance of the data and financial issues. As per this ideas bookkeeping strategies, guidelines, tools that should be characterized in particular report. Figures and numbers should be crucial with exchanges and occasions. Immaterial information and exchanges that are keep beside basic part.
D) Objective of considering depreciation method within a firm
Hardship is simply been said as the derivation and limiting of forecasting of hardware as customary use and characteristic tear and wear. This is attempted for diverse creators in relation to deterioration, a part of the innovators comprehend this as the speculation and few of the innovators think about this as the consumption. Tools that are used in order to measure devaluation.
Straight line strategy: This computes devaluation to remain same and forecasting for the forthcoming year in this tool.
Written Down strategy: There is a specific rate which is provided to identify the deterioration. calculation of deterioration reduce in the forthcoming years. Forecasting of the benefits will not be finished to 0 during the life cycle of the advantages (Scott, 2015).
CLIENT 4
P5 Apply the bank reconciliation process
Bank reconciliation statement
BRS or Bank reconciliation statement is a financial document which is prepared to reconcile bank balance of passbook and bank balance of cash book, the word reconcile define as making one transaction with another. This statement is equipped to understand the differences between the bank balance of both the books. The primary aim of this document is to identify the reasons of deviation in account balances, this statement is made on a specific date when bank passbook is updated (Weil, Schipper and Francis, 2013). The difference in the balances occurs due to few reasons which affects certain transactions and they are mentioned below:
- Errors and omissions are the most common reason due to which few transactions like cheque issued, payment received are affected. Omission is the state when a transaction is mistakenly omitted to record and error is the state when a transaction is wrongly recorded.
- Delay is also considered as the most common reason of deviation in the balances of passbook and cash book. Here delay is referred as the delay from banks in clearance of certain cheques and demand drafts.
- Service charges also leads the difference, as sometimes client is unaware of bank fees which are charged without intimating the customers.
- Interest earned is the amount which is earned by the customer against their deposited amount which sometimes is not communicated with the customers and difference in balances of both the books occurs.
- Fraud detection; it is not important that every time the deviation occurs due to some mistake, sometimes it can be a result of fraud committed by client or the bank. BRS is the key of preventing these frauds.
- Transfer of cash through various sources requires time, if a client immediately records a transaction of payment which is still in the process of transit than it will lead to deviation in both the books.
Bank Reconciliation Statement As on 1december December 2017
| Date | Particulars | Details | Amount |
| 31/12/17 | Bank Balance as per cash book (Dr. Balance) | 19973 | |
| 01/12/17 | Add: opening adjusting figure | 987 | |
| 02/12/17 | Add: deposits | 176 | |
| 06/12/17 | Add: Distinction between adjust of 783 | 9 | |
| 17/12/17 | Add: instalment to Cook | 97 | |
| 29/12/17 | Add: Finding of lease | 260 | 1529 |
| Total | 21502 | ||
| 02/12/17 | Less: 780 | 426 | |
| 02/12/17 | Less:781 | 737 | |
| 05/12/17 | Less: bank charges | 47 | |
| 10/12/17 | Less: standing orders | 137 | |
| 11/12/17 | Less: 310923 | 297 | |
| 24/12/17 | Less: difference of cash deposit (sales) | 1 | |
| 30/12/17 | Less:Payment received from Fred | 119 | 1764 |
| Balance as per passbook (Cr. Balance) | 19738 |
Cashbook of Kendal Ltd. (Bank only)
| Date | particular | amount | Date | particular | amount |
| 01/12/17 | To balance b/d(Balancing figure) | 20208 | 02/12/17 | By 780 | 426 |
| 01/12/17 | To balance adjustment | 987 | 02/12/17 | By 781 | 737 |
| 02/12/17 | To Deposits | 176 | 05/12/17 | By bank charges | 47 |
| 06/12/17 | To difference of balance | 9 | 10/12/17 | By standing orders | 137 |
| 17/12/17 | To cook | 97 | 11/12/17 | By 310923 | 297 |
| 29/12/17 | To rent | 260 | 24/12/17 | By cash deposit | 1 |
| 30/12/17 | By Fred a/c | 119 | |||
| By balance c/d | 19973 | ||||
| 21737 | 21737 |
CLIENT 5
P6 Process to reconcile control accounts
a) Sales ledger control account and purchase ledger control account
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
| To balance b/d (Debit balance) | 12600 | ||
| To credit sales | 152350 | By Transfer to purchase ledger | 330 |
| By Discount allowed | 380 | ||
| By Receipts from debtors | 141610 | ||
| By opening balance | 12600 | ||
| By Sales return | 7320 | ||
| By Bed debts written off | 120 | ||
| By balance c/d (Debit balance) | 2590 | ||
| 164950 | 164950 |
Purchase ledger accountant
| Particular | Amount | Particular | Amount |
| To general ledger control a/c | By opening balance on (Cr. balance) | 9160 | |
| Purchase return | 1110 | Credit purchase | 116500 |
| Payment to creditors | 101010 | ||
| Discount Received | 290 | ||
| To transfer from sales ledger | 330 | ||
| To balance c/d | 22920 | ||
| 125660 | 125660 |
b) Control accounts
Control accounts are prepared to record the transactions with large number of debtors and creditors. Control accounts are considered as a summary in the general ledger. A control accounts are mainly associated with cleaning details and correcting the balance of uncleared accounts.
CLIENT 6
a) Main features of suspense account
There are some key features remain associated as accounts for suspense accounts. Identifying the transactions which remain associated with correcting the balance and imbalance of transactions are the key features of suspense accounts.
b) Trial balance (£)
| Particular | Debit amount | Credit amount |
| Suspense a/c | 110 | |
| Sales | 1100 | |
| Rent paid | 250 | |
| Receivables | 320 | |
| Travel Expenses | 160 | |
| Purchase | 700 | |
| Payables | 350 | |
| Cash at bank | 840 | |
| Capital | 710 | |
| Total | 2270 | 2270 |
(c) suspense account
| Suspense account | |||
| Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
| To White's personal account | 750 | By balance b/d | 330 |
| By John's personal account | 420 | ||
| 750 | 750 |
d) Difference between suspense account and clearing accounts
Both are considered as temporary accounts subject to incorporate incomplete accounts and information.
CONCLUSION
This report is prepared to analyses the essential aspect which remain associated with financial accounting. To investigate as far as finance related bookkeeping and cash related framework also considered in this report. Centrality of twofold area accounting structure as charge and credit. Courses of action and buy exchanges when all is said in done records, preliminary alter and the direct of progress off used to finish the record posting. There is a centrality of trade related bookkeeping portrayed out this novel circumstance. Debilitating systems, get-together and treatment of uncommon costs cleared up in solid based decisions and conditions. Bookkeeping method and structures are examined in regard of sole dealer association, affiliations and obliged affiliations. Bank reconciliation statement and the concept of suspense account also defined in this report. Techniques subject to making final accounts also illuminated in this report. Centrality of strain records and oblige frameworks in regard of record control accounts are delineated in every profitable sense. Asoc check for best coursework help from experts.
REFERENCE
- Bazley, M. and et. al., 2013. Financial Accounting: An Integrated.Thomson Pty Ltd, South Melbourne.
- Beatty, A. and Liao, S., 2014. Financial accounting in the banking industry: A review of the empirical literature.Journal of Accounting and Economics,58(2-3), pp.339-383.
- Bertoni, M. P. G. V. A. G. and De Rosa, B., 2012. Green accounting: an alternative approach to reporting emission trading allowances in financial statements.
- Bhattacharyya, A. K., 2012.Financial accounting for business managers. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd..
- Biondi, Y. and Zambon, S. eds., 2013.Accounting and business economics: Insights from national traditions. Routledge.

























